The healthcare industry is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven mainly by technological advancements transforming how patients are diagnosed, treated, and cared for. From robotics to artificial intelligence (AI), these innovations are improving the quality of care and expanding access to life-saving treatments. In this article, we explore some of the most revolutionary medical technologies that are reshaping the landscape of modern medicine and setting the stage for the future of healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics
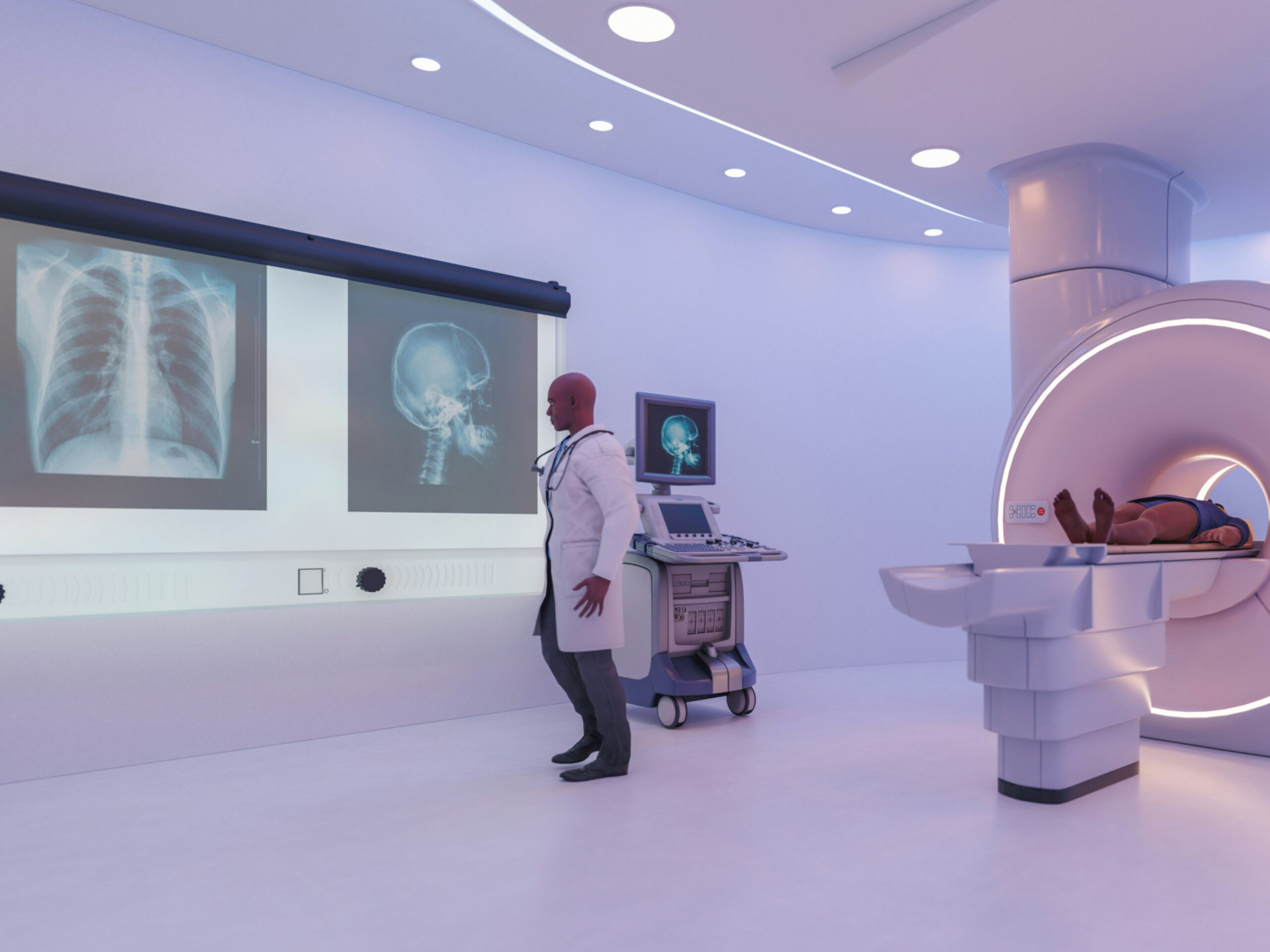
Artificial intelligence has rapidly become one of the most influential forces in modern medicine. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and identify patterns often undetectable by the human eye has led to breakthroughs in diagnostics. AI systems are now being used to analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These systems can detect early signs of diseases like cancer, heart conditions, and neurological disorders, often identifying problems before symptoms appear.
Furthermore, AI-driven diagnostic tools improve efficiency in hospitals and clinics by streamlining workflows. By automating the analysis of diagnostic images and lab results, these tools free up valuable time for healthcare providers to focus on patient care. Additionally, AI algorithms are now being used to predict patient outcomes, helping doctors make more informed decisions about treatment plans. As AI continues to evolve, its ability to enhance diagnostic accuracy and reduce human error will play a pivotal role in improving healthcare outcomes across the globe.
Robotic Surgery and Minimally Invasive Procedures
Robotic surgery has been a game-changer for both surgeons and patients. By offering enhanced precision, smaller incisions, and better visualization, robotic-assisted procedures have significantly improved the quality of surgical care. Surgeons can now perform complex procedures with greater accuracy, even in areas that are difficult to reach using traditional methods. As a result, patients benefit from less trauma, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
One of the primary benefits of robotic surgery is its ability to perform minimally invasive procedures. In contrast to traditional open surgery, which requires large incisions, robotic systems allow for slight, precise cuts. This minimizes blood loss and reduces the risk of complications such as infection. As patients recover more quickly and experience less postoperative pain, the need for extended hospital stays is significantly reduced, leading to lower healthcare costs. Robotic-assisted surgery is particularly beneficial in urology, gynecology, and cardiology, where precision is critical for optimal outcomes.
Wearable Health Devices and Continuous Monitoring
Wearable health devices have become an essential part of modern healthcare, providing real-time monitoring of vital signs and allowing patients to track their health metrics throughout the day. Devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers have evolved from simple activity trackers into advanced tools capable of measuring heart rate, blood oxygen levels, sleep patterns, and even blood glucose levels. These devices empower individuals to take a proactive approach to their health, providing immediate feedback on their well-being.
In healthcare settings, wearables are invaluable for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), for example, allow individuals with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels throughout the day, providing real-time alerts when levels fall outside of the target range. Similarly, wearable heart rate monitors can detect irregularities, such as arrhythmias, and alert patients and healthcare providers to potential health risks. As wearable technology advances, these devices will play an even more significant role in preventing medical emergencies and improving long-term health management.
Telemedicine and Virtual Healthcare
Telemedicine has surged in popularity, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic. This technology allows patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely through video calls, phone consultations, or online messaging platforms. Telemedicine has made healthcare more accessible, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas with limited medical facilities. Patients no longer have to travel long distances to receive care, and healthcare providers can offer consultations from the comfort of their own homes or offices.
Moreover, telemedicine has proven to be an essential tool for managing chronic conditions and providing ongoing care. Patients with conditions like asthma, diabetes, or mental health disorders can benefit from virtual follow-ups and remote monitoring, ensuring that they receive timely support without having to leave their homes. The rise of telemedicine has not only improved access to care. Still, it has also reduced the strain on healthcare facilities, helping to alleviate overcrowding and shorten wait times for in-person visits. As the technology matures, telemedicine will likely become a permanent feature of the healthcare system, offering even greater convenience and accessibility for patients worldwide.
Gene Editing and Precision Medicine
Gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, have ushered in a new era of medicine, offering the potential to treat genetic disorders at their root. By enabling scientists to modify DNA precisely, gene editing promises to cure genetic diseases that were once considered untreatable. For example, researchers are currently exploring gene editing to treat conditions such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
In addition to gene editing, precision medicine is another rapidly growing field that tailors treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and environment. Unlike the traditional “one-size-fits-all” approach, precision medicine aims to customize treatments for each patient, increasing the likelihood of success while minimizing side effects. By understanding the genetic basis of diseases, doctors can prescribe more targeted therapies better suited to the patient’s unique needs. As gene editing and precision medicine continue to advance, they can revolutionize the treatment of various chronic and genetic conditions, offering patients more effective and personalized care.
3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has significantly impacted healthcare, particularly in prosthetics, implants, and surgical planning. By creating custom-made prosthetics and implants tailored to an individual’s specific anatomy, 3D printing has dramatically improved the comfort and functionality of these devices. Unlike traditional methods, which often require generic, one-size-fits-all solutions, 3D printing allows for more personalization, leading to better patient outcomes.
In addition to prosthetics, 3D printing is used in surgical planning and education. Surgeons can create 3D models of patients’ organs or tumors, allowing them to practice complex procedures before performing them on the patient. This improves surgical precision and reduces the risk of complications during surgery. As 3D printing technology advances, its healthcare applications will only expand. Potentially, this will lead to the creation of bio-printed tissues and organs for transplant, further revolutionizing the field of regenerative medicine.
The Future of Medical Technology
The future of medical technology is inspiring, with ongoing innovations that promise to enhance the quality of care and improve patient outcomes. As artificial intelligence, robotics, wearables, and gene editing continue to advance, they will further personalize and optimize healthcare for patients worldwide. Integrating these technologies will help create more efficient, accessible, and effective healthcare systems while making treatments safer and more tailored to individual needs.
As we look ahead, it is clear that technology will play a central role in shaping the future of healthcare. By embracing these revolutionary innovations, we can improve patients’ quality of life, reduce healthcare costs, and address some of the most pressing challenges facing the medical field today. With breakthroughs on the horizon, the possibilities for the future of medicine are limitless.
Revolutionary medical technologies are changing the game by improving patient care, making treatments more precise, and expanding access to life-saving medicines. From AI-driven diagnostics to gene editing and 3D printing, these innovations are transforming healthcare delivery. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements that will continue to shape the future of medicine, making healthcare more effective, accessible, and personalized than ever before.